Muscle strains are a common hurdle for athletes, as both a physical and psychological impediment. This blog post unpacks seven effective strategies to expedite recovery from muscle strains. Our goal is not just to outline these techniques but to delve into how they function, providing athletes with a deeper understanding and practical ways to implement them.
Understanding the mechanics behind muscle strain recovery is critical for athletes. It’s not just about quick fixes but about adopting strategies that align with the body’s natural healing processes. This knowledge empowers athletes to take proactive steps in their recovery, ensuring they return to their sport stronger and more resilient.
Contents
1. Rest and Recovery Time
Rest is the cornerstone of recovering from a muscle strain. It’s during this period of inactivity that the body starts repairing the damaged muscle fibers. Overlooking the need for rest can exacerbate the injury, leading to prolonged recovery or even further damage.
Balancing Rest with Activity
However, rest doesn’t mean complete immobility. It’s about finding the balance between giving the injured muscle time to heal and keeping it gently active to promote blood flow. Light activities, like walking or stretching, can be beneficial if done correctly and with a healthcare provider’s guidance.
For those interested in exploring advanced recovery technologies, oxyhelp.com offers a unique solution. Capable of accommodating multiple users simultaneously, this chamber provides an environment where an assistant or observer can monitor and assist during the session, catering to both individual and group therapy needs.
2. Ice and Heat Therapy
Immediately after a muscle strain, ice is your best friend. Applying ice to the injured area reduces swelling and numbs the pain. The cold constricts blood vessels, limiting inflammation and the accumulation of fluids in the tissue.
Transitioning to Heat Therapy
After the initial phase, heat becomes more beneficial. Heat therapy enhances blood flow to the injured area, which accelerates healing by bringing in nutrients and oxygen. Warm baths, heat packs, or heating pads can be used, but it’s crucial to avoid applying heat too soon as it can increase swelling.
3. Compression and Elevation
Compression garments or bandages provide support to the injured muscle, reducing swelling and offering slight immobilization. This helps in keeping the muscle in a relaxed state, which is vital for recovery.
Elevation to Reduce Swelling
Elevation, ideally above heart level, further assists in reducing swelling. It leverages gravity to drain excess fluid away from the injured area, speeding up the reduction of inflammation and aiding in pain relief.
4. Proper Nutrition and Hydration
Nutrition is a powerful tool in muscle recovery. A diet rich in proteins, vitamins, and minerals supports the body’s repair process. Protein is particularly crucial as it’s the building block of muscle tissue.
Hydration for Optimal Recovery
Staying hydrated is equally important. Water plays a key role in transporting nutrients to the injured area and in removing waste products. Dehydration can slow down the healing process and should be avoided.
5. Physical Therapy and Stretching
Engaging in physical therapy under professional guidance can significantly speed up recovery. A therapist can provide targeted exercises that strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility, reducing the risk of re-injury.
Incorporating Stretching into Recovery
Stretching, when done correctly, can alleviate stiffness and improve range of motion. It should be approached gently, focusing on gradual improvement rather than pushing the muscle too far.
6. Gradual Return to Activity
Rushing back into full activity is a common mistake. A gradual return allows the muscle to adapt and strengthen. This approach minimizes the risk of re-injury and helps in building confidence in the muscle’s capability.
Listening to Your Body
Listening to your body’s signals is vital. Pain or discomfort during an activity is a clear sign to step back. It’s about progressing at a pace that the body can handle, not the mind.
7. Mental Health and Coping Strategies
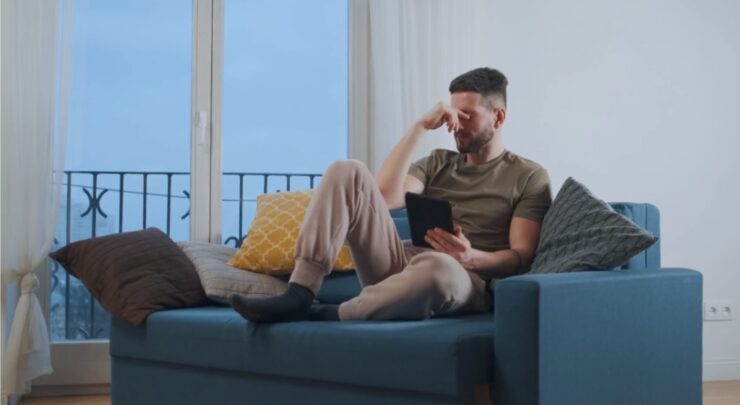
Recovering from a muscle strain isn’t just a physical challenge; it’s a mental one too. Acknowledging the psychological impact and adopting coping strategies can play a significant role in the overall recovery process.
Implementing Coping Strategies
Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and positive visualization can help in managing stress and maintaining a positive outlook. These practices aid in keeping motivation levels high and promote a healthier, more holistic recovery process.
Preventing Future Injuries
Every injury offers a learning opportunity. Understanding what led to the strain can help in preventing future occurrences. This might involve analyzing your training methods, equipment, or even daily habits that could contribute to muscle strain.
Preventive Measures
Prevention is better than cure. Incorporating regular strength training, ensuring proper warm-up and cool-down routines, and paying attention to body mechanics can significantly reduce the risk of future muscle strains. It’s also important to listen to your body and give it the necessary rest to recover from strenuous activities.
The Role of Supplements in Recovery
Certain supplements can aid in muscle recovery. For instance, Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties, and protein supplements can assist in muscle repair. However, it’s essential to choose supplements wisely and preferably under professional guidance.
The Limits of Supplements
Supplements can help with your recovery, but they shouldn’t take the place of a balanced diet and a comprehensive recovery plan. Think of them as a helpful addition, not the whole solution.
Balancing Rest with Rehabilitation
Active recovery, a balance between rest and rehabilitation exercises, is crucial. Under professional guidance, light exercises can keep muscles active without overstraining them. This approach aids in maintaining flexibility, strength, and blood flow to the injured area.
Tailoring Rehabilitation to Individual Needs
It’s important to tailor rehabilitation exercises to individual needs. What works for one athlete might not work for another. A personalized recovery plan, developed with a healthcare provider, ensures that the exercises are effective and safe for your specific injury.
The Psychological Aspect of Recovery
Mental health is a critical component of recovery. Stress, anxiety, and frustration are common during this period. Addressing these emotions through counseling, meditation, or simply talking about them is important for a holistic recovery.
Staying Positive and Motivated
Maintaining a positive mindset and staying motivated can significantly influence recovery. Setting small, achievable goals and celebrating progress can help maintain a positive outlook. Surrounding yourself with positive influences and motivational resources can also be beneficial.
Final Words
Healing from a muscle strain is about more than just physical recovery; it’s a journey that involves rest, the right therapy, good nutrition, and taking care of your mental well-being.
Incorporate these tips into your recovery routine, and you’ll not just speed up your healing but also gear up to return to your sport stronger and more ready than ever. Keep in mind, that it’s not just about getting better but about building resilience for whatever comes next.